C# でマルチスレッド対応の Logクラスを紹介します。また、ログの書き込み処理を別スレッドに実装し、ログ書き込み負荷を抑えます。スレッドセーフとはマルチスレッドでどんなタイミンクでコールされても機能が保証されていることを示します。

概要
最近は言語側で非同期呼び出し機能が実装されたことにより、マルチスレッドを活用したプログラムが一般的になってきています。
ログは複数のスレッドからコールされ、コール順序順にログが書かれることが期待されます。単純に排他ロックをかけてログを書き込む場合、他のスレッドが待ち状態になりスレッドの平行動作を阻害することになりパフォーマンス低下につながります。
そのため、各スレッドはキューに書き込み、ログ書き込み用スレッドがキューからログを取得してファイルへの書き込む構造でクラス設計をします。キューに積むところだけ排他します。
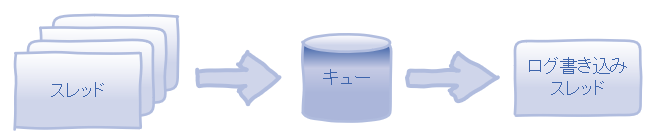
ログクラス
C#では非同期スレッド生成のために Task クラスから起動するのが一般的ですが、これはスレッドプールから割り当てるための仕組みで、スレッド生成までに待たされる場合があります。
今回のようにスレッドをサーバーとして常駐させるケースには、素直にスレッドを生成したほうが確実です。
キューには ConcurrentQueue クラスを使用します。このキューはスレッドセーフなので排他しなくてもよいため、今回のようなスレッド間の非同期な情報伝達には最適です。
唯一排他をしているのは時刻取得とキューへのセットの箇所です。この排他がないとログが時間順に並ばない恐れがあります。
ログを書き込むスレッドに対しては、イベントを使用して通知を入れます。ここでのイベントはC# の event ではなく、Windowsオブジェクトのイベントです。ログスレッドはこのイベントが発生するまで待機します。
using System; using System.IO; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Collections.Concurrent; public class Log : IDisposable { internal class LogInfo { public DateTime dt; public int threadID; public string msg; } string filepath; StreamWriter sw; ConcurrentQueue<LogInfo> que; EventWaitHandle evt; Thread th; volatile bool endlflag; public Log(string filepath) { this.filepath = filepath; this.sw = new StreamWriter(filepath, true); this.que = new ConcurrentQueue<LogInfo>(); this.evt = new EventWaitHandle(false, EventResetMode.AutoReset); this.endlflag = false; this.th = new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.logthread)); this.th.IsBackground = true; this.th.Start(); } ~Log() { this.Dispose(); } public void Dispose() { if (this.sw != null) { this.endlflag = true; this.evt.Set(); this.th.Join(); this.sw.Close(); this.sw.Dispose(); this.sw = null; } } public void Add(string msg) { if (this.sw == null) return; if (msg == null) return; if (msg == "") return; LogInfo x = new LogInfo() { msg = msg, threadID = System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, }; lock (this) { // ログ上の時間とキュー登録順序を保証する x.dt = DateTime.Now; this.que.Enqueue(x); } this.evt.Set(); } void logthread() { int timeout = -1; while (true) { bool ret = this.evt.WaitOne(timeout); // イベント待ち if (!ret) { this.sw.Flush(); // タイムアウト時はファイルをフラッシュ timeout = -1; // 次回はイベント無限待ち continue; } // イベント発生時 while (this.que.TryDequeue(out LogInfo x)) { string str = String.Format( "{0}: {1}: {2}", x.dt.ToString("yy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss.fff"), x.threadID.ToString(), x.msg ); // Console.WriteLine(str); this.sw.WriteLine(str); } if (this.endlflag) { break; } timeout = 5000; // 5sec 後にフラッシュ } } }
呼び出し例
10個のスレッドから連続してログ追加をした例です。
class Test { Log log; void threadfnc() { while (true) { this.log.Add("test"); // 10個のスレッドからログを追加 Thread.Sleep(10); } } void Run() { this.log = new Log(@"c:\temp\log.txt"); Task[] t = new Task[10]; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { t[i] = Task.Run(threadfnc); } Task.WaitAll(t); this.log.Dispose(); } }